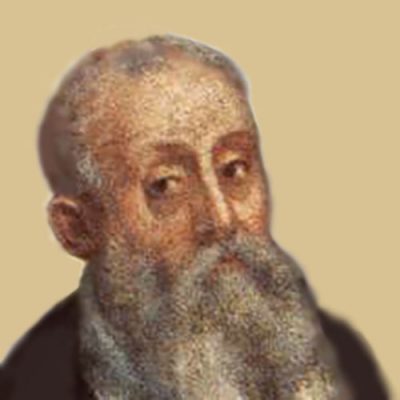
Agnolo di Cosimo (Italian: [ˈaɲɲolo di ˈkɔːzimo]; 17 November 1503 – 23 November 1572), usually known as Bronzino (Italian: Il Bronzino [il bronˈdziːno]) or Agnolo Bronzino,[a] was an Italian Mannerist painter from Florence. His sobriquet, Bronzino, may refer to his relatively dark skin[1] or reddish hair.[2]
He lived all his life in Florence, and from his late 30s was kept busy as the court painter of Cosimo I de’ Medici, Grand Duke of Tuscany. He was mainly a portraitist but also painted many religious subjects, and a few allegorical subjects, which include what is probably his best-known work, Venus, Cupid, Folly and Time, c. 1544–45, now in London. Many portraits of the Medicis exist in several versions with varying degrees of participation by Bronzino himself, as Cosimo was a pioneer of the copied portrait sent as a diplomatic gift.
He trained with Pontormo, the leading Florentine painter of the first generation of Mannerism, and his style was greatly influenced by him, but his elegant and somewhat elongated figures always appear calm and somewhat reserved, lacking the agitation and emotion of those by his teacher. They have often been found cold and artificial, and his reputation suffered from the general critical disfavour attached to Mannerism in the 19th and early 20th centuries. Recent decades have been more appreciative of his art.